LLM Application for Math & Reasoning
Paper Title

Authors
Simon Frieder et. al.
Affiliations
U of Oxford et. al.
Date
Dec 7, 2023
Abstract
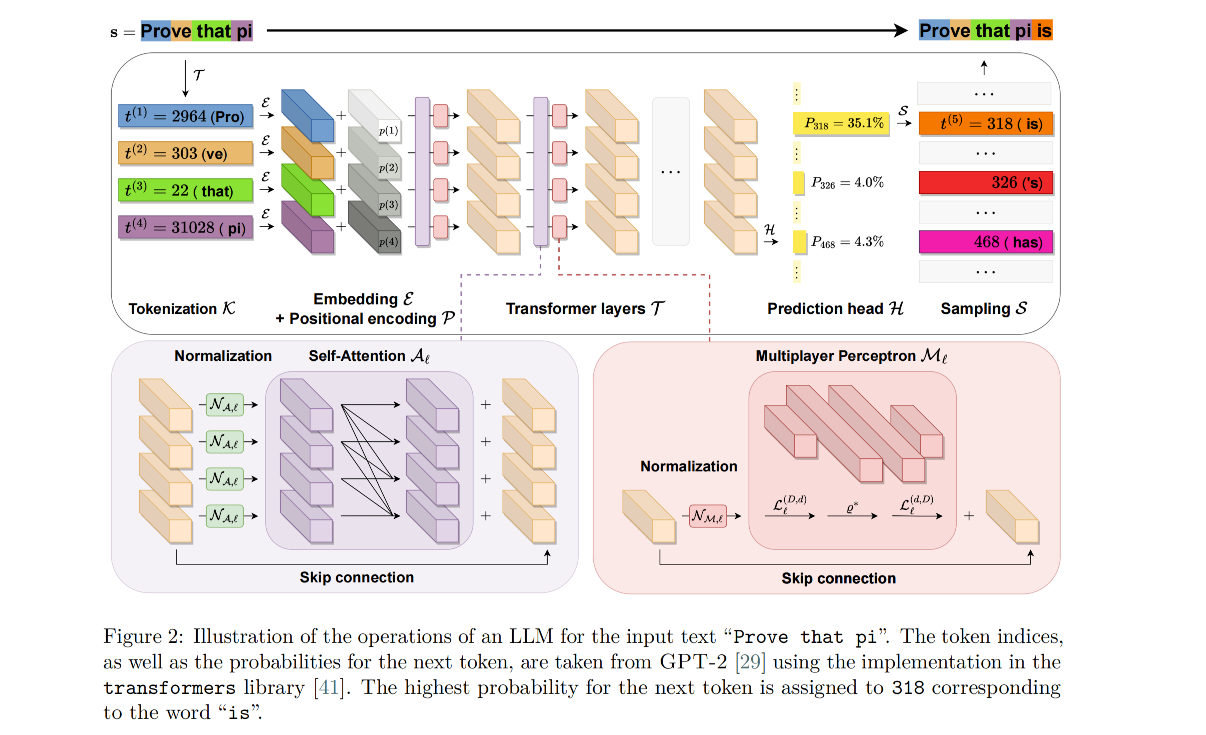
Large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT have received immense interest for their general purpose language understanding and, in particular, their ability to generate high-quality text or computer code. For many professions, LLMs represent an invaluable tool that can speed up and improve the quality of work. In this note, we discuss to what extent they can aid professional mathematicians. We first provide a mathematical description of the transformer model used in all modern language models. Based on recent studies, we then outline best practices and potential issues and report on the mathematical abilities of language models. Finally, we shed light on the potential of LMMs to change how mathematicians work.
LLM for Mathematics
- Literature / Search Engine
- Brainstorming / Idea Generation
- Proof Checking
- Collaborative writing
Conclusion
Our study has highlighted how LLMs possess a remarkable capacity to assist mathematicians in various ways, from detecting and filling gaps in theorems to acting as search engines and finding definitions from descriptions of mathematical objects. We have shed light on the inner mechanism of the core piece of architecture that powers modern LLMs, the transformer, and how the way they produce an answer to mathematical questions differs starkly from human reasoning.
5Ws
1. What is the problem?
The paper discusses the potential and limitations of LLMs, like ChatGPT and GPT-4, in assisting mathematicians. It explores how these models can be integrated into mathematical work, focusing particularly on their ability to understand and solve mathematical problems, and generate mathematical proofs.
2. Why is the problem IMPORTANT?
The integration of LLMs in mathematics is important as it represents a significant shift in how mathematical problems can be approached and solved. LLMs offer a new tool for mathematicians, potentially speeding up research, providing novel insights, and making mathematics more accessible. This integration could lead to significant advancements in the field and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of mathematical research and education.
3. Why is the problem DIFFICULT?
The problem is difficult due to the inherent nature of mathematical reasoning, which requires high precision and logic. LLMs, being based on language understanding, may struggle with the exactness required in mathematical proofs. Additionally, the autoregressive nature of LLMs means they don't typically revise their outputs, which can be problematic in mathematics where revision and iterative refinement are common. LLMs also struggle with arithmetic computations and might provide valid proofs for slightly different problems than the ones posed.
4. What are the OLD techniques?
Traditional techniques in mathematics involve human-driven research, problem-solving, and theorem proving without the aid of advanced AI tools. This includes manual computations, logical reasoning, and proof development, often requiring extensive time and effort.
5. Advantages and Disadvantages of the new techniques compared to the old ones?
Advantages:
- LLMs can process and analyze vast amounts of data quickly, potentially accelerating research.
- They can assist in detecting gaps in theorems, act as advanced search engines for mathematical literature, and aid in brainstorming or idea generation.
- LLMs make mathematics more accessible to a broader audience by allowing interaction in natural language.
Disadvantages:
- LLMs may produce errors in mathematical reasoning due to their probabilistic nature and lack of deep understanding of mathematical logic.
- They are less reliable for complex mathematical proofs, particularly those requiring high precision.
- LLMs might reinforce biases in research by favoring more popular or commonly discussed ideas.